-Technology
Understanding Solar Inverters: On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Systems in Singapore
- WP_admin
- Oct 16, 2024
As Singapore progresses toward a sustainable energy future, solar inverters play a crucial role in converting solar energy into usable electricity. Understanding the different types of solar inverters—on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid—is essential for homeowners and businesses considering solar energy systems.

What is a Solar Inverter?
A solar inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is used by most household appliances and the electrical grid. The type of inverter you choose will depend on your energy needs and whether you want to connect to the grid.
Types of Solar Inverters
On-Grid Inverters:
Overview: On-grid inverters, also known as grid-tied inverters, connect directly to the utility grid. They allow homeowners to use solar energy and feed any excess power back into the grid.
Benefits:
Benefits
Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive to install since they do not require batteries for energy storage.
Net Metering: Homeowners can take advantage of net metering policies, which allow them to earn credits for the energy they supply to the grid, effectively lowering their electricity bills.
Simplicity: These systems are straightforward and easy to maintain, relying on the grid as a backup power source.
Off-Grid Inverters:
Benefits
Energy Independence: Ideal for remote locations or areas where grid access is unreliable or unavailable.
Self-Sufficiency: Homeowners can rely solely on solar power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Flexibility: Off-grid systems can be customized based on specific energy needs and can be expanded as necessary.
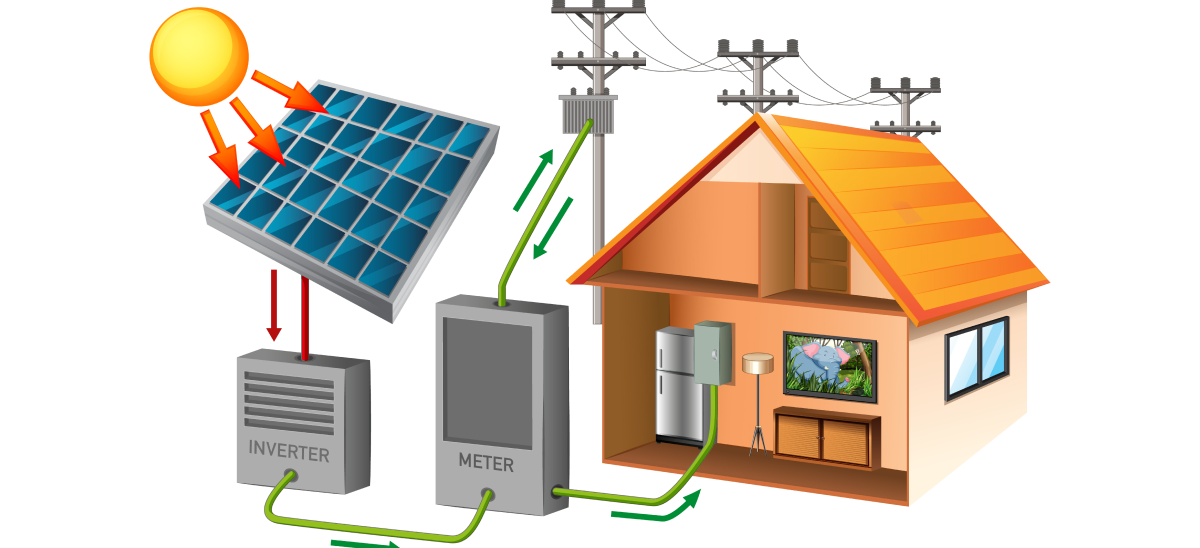
Hybrid Inverters:
Overview: Hybrid inverters combine features of both on-grid and off-grid systems. They can connect to the grid while also managing battery storage, allowing users to store excess energy generated by their solar panels.
Benefits
Versatility: Hybrid inverters provide the flexibility to use solar energy, store it for later use, and sell excess energy back to the grid.
Backup Power: In the event of a power outage, hybrid inverters can draw from the battery to provide electricity, ensuring continuous power supply.
Optimal Energy Management: These systems enable users to optimize their energy usage, balancing consumption between stored energy, solar generation, and grid power.
Choosing the Right Solar Inverter
Energy Needs: Assess your household’s energy consumption to determine the most suitable inverter type.
System Configuration: Decide whether you want a grid-connected system for cost savings, an off-grid system for energy independence, or a hybrid system for flexibility.
Warranty and Support: Choose reputable brands that offer solid warranties and customer support to protect your investment.

Conclusion



